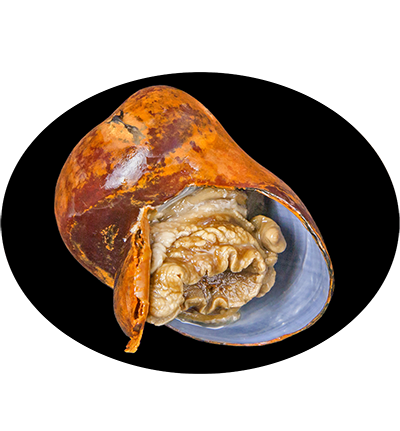
Gigantopelta aegis is a species of deep-sea snail in the family Peltospiridae, found in hydrothermal vent ecosystems, particularly in the Longqi hydrothermal vent field on the Southwest Indian Ridge. This species is adapted to extreme environments, relying on a symbiotic relationship with chemosynthetic bacteria housed in its gills. These bacteria oxidize sulfur compounds from vent fluids to produce organic matter, providing essential nutrients to the snail. Gigantopelta aegis plays a crucial role in vent ecosystems by contributing to nutrient cycling and supporting microbial and faunal communities.
Animalia (Kingdom); Mollusca (Phylum); Gastropoda (Class); Vetigastropoda (Subclass); Neomphalida (Order); Neomphaloidea (Superfamily); Peltospiridae (Family); Gigantopelta (Genus); Gigantopelta aegis (Species)
Gigantopelta aegis C. Chen, K. Linse, Roterman, Copley & A. D. Rogers, 2015
1. Chen C, Linse K, Roterman C N, et al. A new genus of large hydrothermal vent-endemic gastropod (Neomphalina: Peltospiridae)[J]. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 2015, 175(2): 319-335. (Chen et al., 2015)
Shell: Shell globose, three to four whorls, coiled tightly with a deep suture. Spire depressed. Aperture roughly circular, very large. Ratio of shell diameter to aperture length approximately 1:0.633 (average of 100 specimens). Shell trochiform to neritiform, holostomous. Protoconch consists of 0.5 whorls, diameter about 210 μm. Irregular reticulate ornament present initially, becoming obsolete distally. Suture around protoconch very deep. Teleoconch smooth, no distinct sculpture. Subtle growth lines, irregular protuberances present. Growth lines stronger on the body whorl, especially near the aperture. Periostracum thick, dark olive, enveloping the aperture. Ostracum and hypostracum milky white. Thin, fragile without periostracum. Columellar folds lacking. Callus extends to slightly cover columellar. Area around callous concave. Maximum shell diameter 45.7 mm.
Giganteus (Latin), gigantic; Pelta (Latin), shield. This refers to the extremely large adult shell size of the species in this genus for the family Peltospiridae. The genus name is feminine.
Only known from hydrothermal vents on segment E2 (56°05.2′S to 56°05.4S, 30°19.00′W to 30°19.35′W) and E9 (60°02.50′S to 60°03.00′S, 29°58.60′W to 29°59.00′W) of ESR. This species forms dense aggregations rather close to vent effluents.
| Species | Phylum | Common Name | Ecosystem | Depth | Habitat | NCBI Taxonomy ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gigantopelta aegis | Mollusca | deep-sea hydrothermal vent snail | Hydrothermal vent | >2,761 | Longqi hydrothermal vent field (37.7839°S, 49.6502°E) on the Southwest Indian Ridge | 1735272 |
| Genome Assembly | Genome Size | Assembly level | Released year | WGS accession | Submitter | BioProject | BUSCO completeness (%) | Scaffold/Contig N50 (kb) | GC content (%) | Repeat Rate (%) | Gene Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gae_host_genome | 1.1Gb | Chromosome | 2021 | JAEHGF01 | Hong Kong University of Science and Technology | PRJNA612619 | 94.60 | 81,591/461.8 | 37 | 56 | 22,556 |
| Title | Journal | Pubmed ID |
|---|---|---|
| Hologenome analysis reveals dual symbiosis in the deep-sea hydrothermal vent snail Gigantopelta aegis | nature communications | 33608555 |
| Gene ID | Description |
|---|---|
| ctg1733-0.2-1 | ENDONUCLEASE-RELATED |
| ctg1734-0.5-1 | BTB/POZ DOMAIN-CONTAINING |
| ctg1736-0.5-1 | PROTEASE M1 ZINC METALLOPROTEASE |
| ctg1737-0.0-1 | PROTEIN CBG26694 |
| ctg1737-0.3-1 | POLYCYSTIN FAMILY MEMBER |
| ctg1738-0.0-1 | FACT COMPLEX SUBUNIT SSRP1 |
| ctg1738-0.4-1 | INHIBITOR OF APOPTOSIS |
| ctg174-1.0-1 | POLYCYSTIN-1 |
| ctg174-1.1-1 | - |
| ctg174-1.2-1 | - |
| ctg174-1.3-1 | - |
| ctg174-4.8-1 | N-ACETYLGALACTOSAMINYLTRANSFERASE |
| ctg174-6.1-1 | HILLARIN |
| ctg174-6.4-1 | ALPHA-(1,3)-FUCOSYLTRANSFERASE C-RELATED |
| ctg1740-0.0-1 | NEUROTRANSMITTER GATED ION CHANNEL |
| ctg1740-0.5-1 | - |
| ctg1740-1.4-1 | FIBRINOGEN/TENASCIN/ANGIOPOEITIN |
| ctg1740-1.5-1 | - |
| ctg1740-2.10-1 | FIBRINOGEN ALPHA CHAIN |
| ctg1740-2.3-1 | FIBRINOGEN/TENASCIN/ANGIOPOEITIN |

